Abstract
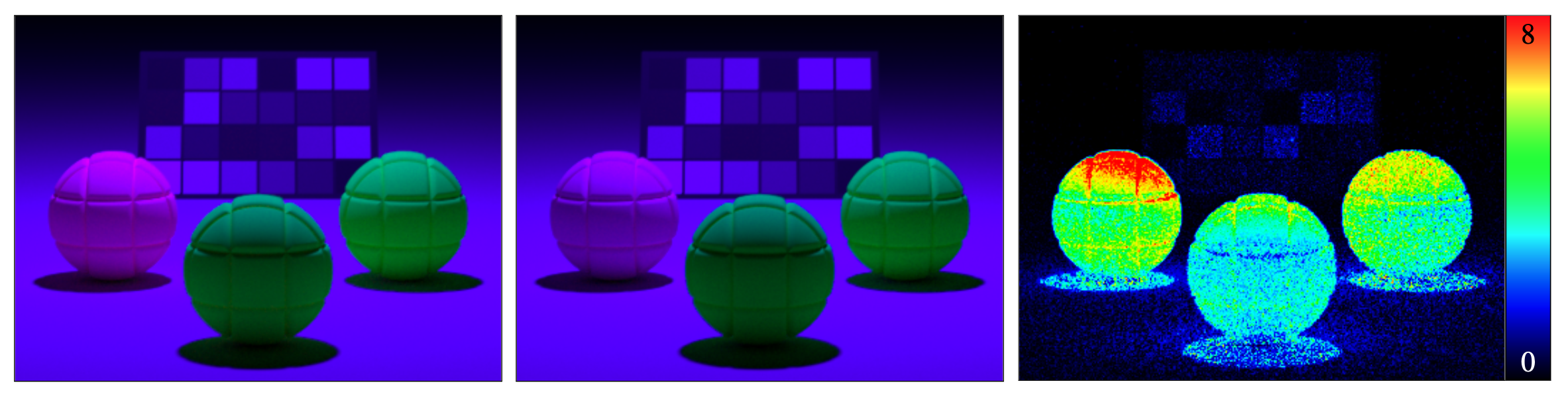
We propose a technique to efficiently importance sample and store fluorescent spectral data. Fluorescence behaviour is properly represented as a re-radiation matrix: for a given input wavelength, this matrix indicates how much energy is re-emitted at all other wavelengths. However, such a 2D representation has a significant memory footprint, especially when a scene contains a high number of fluorescent objects or fluorescent textures. We propose to use Gaussian Mixture Domain to model re-radiation, which allows us to significantly reduce the memory footprint. Instead of storing the full matrix, we work with a set of Gaussian parameters that also allow direct importance sampling. When accuracy is a concern, one can still use the re-radiation matrix data, and just benefit from importance sampling provided by the Gaussian Mixture. Our method is useful when numerous fluorescent materials are present in a scene, and in particular for textures with fluorescent components.